acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy trial|acetabular labrum repair : mail order This single-surgeon, parallel randomized controlled trial included patients aged ≥40 years with limited osteoarthritis (Tönnis grades 0-2) who were randomized 1:1 to arthroscopic . Jacobina 24 horas. 4,359 likes · 18 talking about this. Notícias de Jacobina
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 3 dias atrás · Home. |. "It Doesn't End Here" Welcome to the The 100 Wiki – a collaborative database dedicated to the The 100! This wiki can be edited by anyone, and is run by a team of dedicated fans just like you! This wiki currently housing 824 articles and 20,470 files. There are 10 active users .
The purpose of this study was to determine (1) the diagnostic accuracy of MRI and MRA for the detection of ALT, (2) whether 1.5 T or 3.0 T is all acceptable, by conducting a .Prevalence of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% (Narvani et al., 2003) and 55% (McCarthy et al., 2001).
custom diy soil moisture meter
A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had . Conclusions: Acetabular labral injury is closely correlated with femoro‐acetabular impingement. Impingement tests and MRA have high sensitivity and accuracy in clinical . This single-surgeon, parallel randomized controlled trial included patients aged ≥40 years with limited osteoarthritis (Tönnis grades 0-2) who were randomized 1:1 to arthroscopic .
Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single .
custom does a moisture meter detect mold
Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22–55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is .The FADIR test is commonly used in the assessment of hip pathology, espeially femoroacetabular impingement and labral tear. However, due to high sensitivity and low specificity of the test, it is important to understand its limitations and consider its role in conjunction with other tests and diagnostic tools when assessing hip pathology [1] .The goal during physical therapy of an acetabular labral tear is to optimize the alignment of the hip joint and the precision of joint motion . This can be done by: . Hölmich P, Thorborg K. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the .
custom electronic moisture meter
There are many special tests of the hip joint that may have . a labral tear, is far less accurate and often needs to be paired with other diagnostic modalities [33, 34, 38, 39, 41]. Often, years may pass before an acetabular labral tear is diagnosed. Imaging and Diagnostic Testing Given theabove-suspected etiologiesoflabralpathology,itis
Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22–55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. An ALT can lead to biomechanical deficiencies and a loss of stability to the coxafemoral joint due to the labrum serving as a stabilising structure of this . A recently published randomized controlled trial demonstrated that for patients over the age of 40 years, with minimal osteoarthritis and a symptomatic acetabular labral tear, surgery with postoperative physiotherapy guided rehabilitation delivered superior outcomes at 12 months when compared to a focused physiotherapy programme alone. 15 . The acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous, horseshoe-shaped structure of fundamental importance [1,2,3,4].It increases the joint contact surface area by means of a 22% upscale of the articular surface [].However, perhaps the most fundamental features of the labrum are derived from the suction seal mechanism it provides.Examination of acetabular labral tear: a continued diagnostic challenge . in the involved hip as a result of the increased length of the lever arm this muscle has to function across.122 SPECIAL TESTS At this point in the examination (after the red flags and potential contribution from the lumbar spine and pelvic girdle have been excluded .
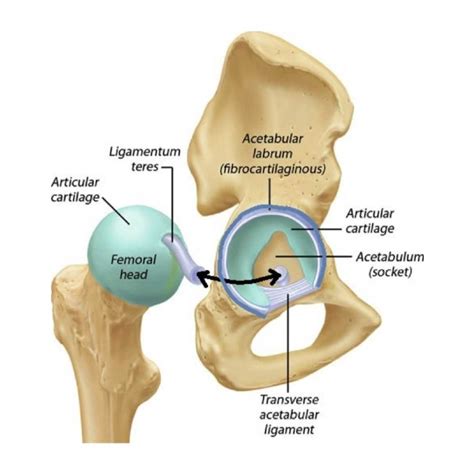
The hip is a uniquely constrained joint with critical static stability provided by the labrum, capsule and capsular ligaments, and ligamentum teres. The labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure along the acetabular rim that encircles most of the femoral head. Labral tears are localized based on the clock-face method, which determines the extent of the .
The most common special tests to assess for FAI include the anterior impingement . It is important to have clear and accurate communication with all members treating FAI syndrome. . Blatz D, Karam C, et al. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Acetabular Labral Tear of the Hip: A Pilot Study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019 Nov;98 .
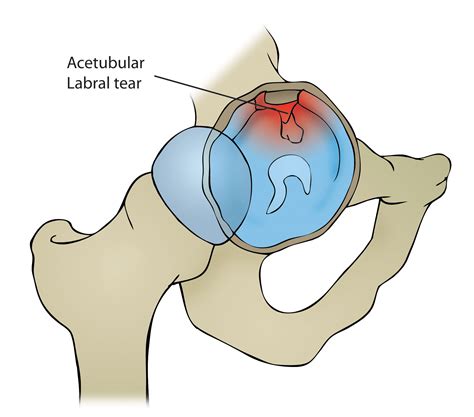
The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique [edit | edit source] . The validity and accuracy of clinical diagnostic tests used to detect labral pathology of the hip: a systematic review. Manual therapy. 2011 Aug 1;16(4):318-26. Diagnostic Accuracy of Clinical Tests for Hip Instability. TABLE 3 provides the diagnostic accuracy of 5 clinical tests for hip instability assessed in 2 studies. 13, 28 Positive LRs to diagnose or rule in hip instability ranged from 2.2 (foot progression angle walking test) to 15.9 (prone instability test) . Negative LRs to exclude or rule out .
labral tear diagnosis
acetabular tear labrum
Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip femoroacetabular impingement/labral tear: a systematic review with meta-analysis Br J Sports Med . 2015 Jun;49(12):811. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2014-094302.The concave, cup-shaped acetabulum (part of the pelvis) is the “socket.” The rounded head of the femur fits inside the cup-shaped acetabulum. When you move your hip, the head of your femur rotates within the acetabulum. The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum.
Background This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the current evidence on the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA for detecting acetabular labral tears (ALT). Methods We systematically searched the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane library until February 5, 2021, to identify original research studies reporting the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA for the .
acetabular labrum repair
Acetabular labral tear, as the name implies, is a tear involving the acetabular labrum of the hip. . most accurate imaging study (91% vs 36% on native MRI) minimally invasive compared with arthroscopy. highly diluted . If this test is negative and if a labral tear is still suspected, ultrasound can reliably diagnose most tears of the acetabular labrum. . and accuracy of MR arthrographic findings compared to those of hip arthroscopy (Chan et al. 2005, Freedman et al. 2006, . indicates that a learning curve may be associated with the use of ultrasound in . A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
A hip (acetabular) labral tear is damage to cartilage and tissue in the hip socket. The labrum is a band of tough cartilage and connective tissue that lines the rim of the hip socket, or acetabulum.
Special Tests. Anterior Hip Impingement Test: Hip . et al. Lesions of the acetabular labrum: accuracy of MR imaging and MR arthrography in detection and staging. Radiology 1996;200(1):225–230 . Karam C, Gustin Z, Gordon AH. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Acetabular Labral Tear of the Hip: A Pilot Study. Am J Phys Med . All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests. Although a positive McCarthy test is not very common in labral lesions, it has a high specificity.
The acetabular labrum can tear through sudden major trauma to the hip joint, or through repeated minor trauma (such as high impact sports). . which is an MRI scan combined with injecting the hip joint with a special dye, may sometimes be required – this has a diagnostic accuracy of about 90%. MR-arthrogram showing a labral tear (the white .Systematic review The validity and accuracy of clinical diagnostic tests used to detect labral pathology of the hip: A systematic review Roanna M. Burgessa,*, Alison Rushtonb, Chris Wrightb, Cathryn Daborna aRegional Medical Centre, Royal Air Force Cosford, Wolverhampton WV7 3EX, UK b School of Health and Population Sciences, College of Medical and Dental Sciences, The . INDICATIONS. In the hip preservation setting, irreparable and non-viable labral tears have been suggested as the main indicators for labral reconstruction, a situation that mostly manifests in revision cases (Fig. 1).Herickhoff and Safran [] reported that the intraoperative appearance of the labrum is the single most important factor for labral treatment decisions.
PURPOSE: To determine the accuracy of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR arthrography in the detection and staging of lesions of the acetabular labrum. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Fifty-seven hips of 56 patients with chronic hip pain and a strong clinical suspicion of labral lesions were examined with a three-dimensional gradient-echo sequence in .
Evidence Regarding Orthopaedic Clinical/Special Tests. A systematic review by Reiman et al (2012) . Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests of the hip: a systematic review with meta-analysis. . Examination of acetabular labral tear: a continued diagnostic challenge. Br J Sports Med. 2013 Jul 31. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091994. [Epub ahead . Figure 4-1 Classifications of acetabular labral tears: radial flap, radial fibrillated, and peripheral longitudinal. (Adapted from Lage LA, Patel JV, Villar RN. The acetabular labral tear: an arthroscopic classification. Arthroscopy. 1996;12:269-272.) The primary risk factors identified for acetabular labral tears are anatomic variants that affect hip joint function and .The acetabular labrum is a fibrous rim of cartilage around the hip socket that is important in normal function of the hip. It helps keep the head of the femur (thigh bone) inside the acetabulum (hip socket). It provides stability to the joint. Our understanding of the acetabular labrum has expanded just in the last 10 years.
custom elephant ear moisture meter
custom false moisture meter readings drywall
RESULTADOS POR LOCALIDADE (Estado ou Banca) Rio d.
acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy trial|acetabular labrum repair